ADAS Overview
The Basics of ADAS
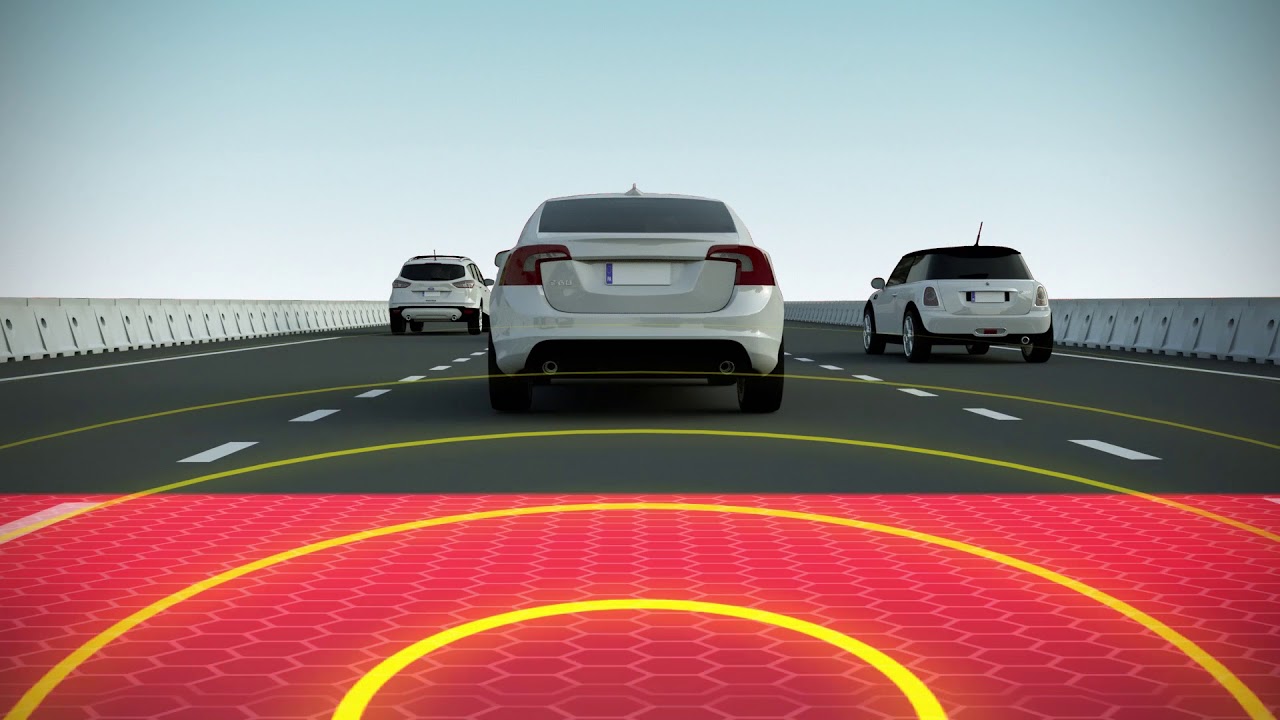
What is ADAS?
An Advanced Driver-Assistance System also known as ADAS is a sophisticated network of electronic technologies for modern vehicles intended to automate certain aspects of driving and improve driver situational awareness in order to increase safety.
ADAS employs radar, sensors and cameras to assess a vehicle's speed, tendencies and environment. This information is used to reduce the driver's recognition time, processing time, decision time and response time.
Why is ADAS important?
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, driver error is a factor in 94% of vehicle crashes, making human error the leading cause of accidents. ADAS was developed to improve safety by providing warnings, alerts and other assistance to the driver. Recent research indicates that ADAS technology, properly employed and maintained, is significantly reducing the outcome of accidents.

Did you know?
Evolution of Vehicle Technology
Anti-Lock Brakes (ABS) made it possible to create an Electronic Stability Control (ESC), which required an ABS system, steering angle sensor and other sensors. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) and Lane Departure (LDW) were made possible through the development of radar, laser and camera-based technology.
Types of ADAS systems: Passive vs. active
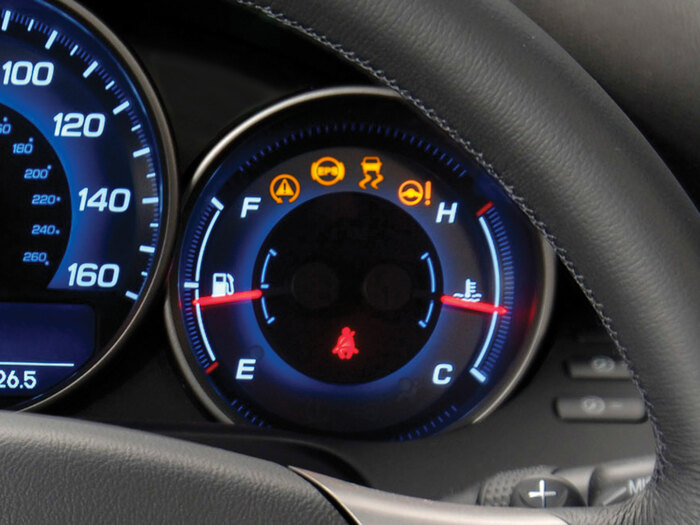

Passive
Passive refers to features that are designed to alert the driver but do not actively control vehicle movements. Common passive ADAS features include anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC) and tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS).
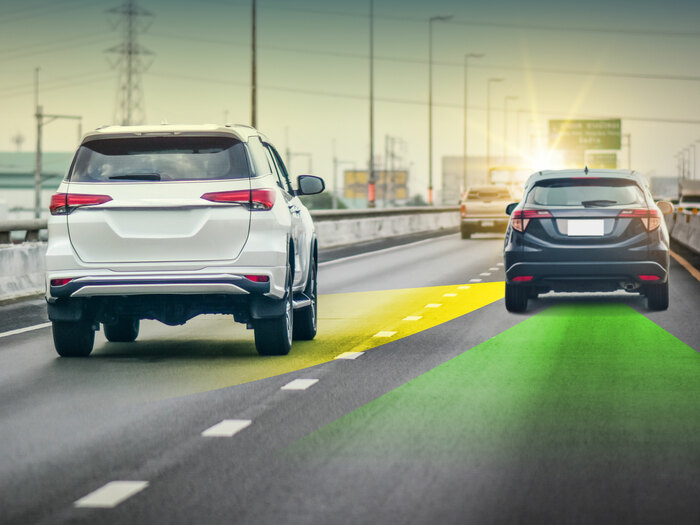

Active
Active refers to features that take actionable steps to avoid potential accidents. Common active ADAS features include adaptive cruise control (ACC), automatic emergency braking (AEB), blind spot monitoring (BSM) and lane departure warnings (LDW).
Benefits of ADAS
- Improved driver assistance
- Reduced human driving errors
- Increased environmental awareness
- Enhanced road safety
- Fewer collisions
- Reduced injuries and fatalities
- Improved traffic management
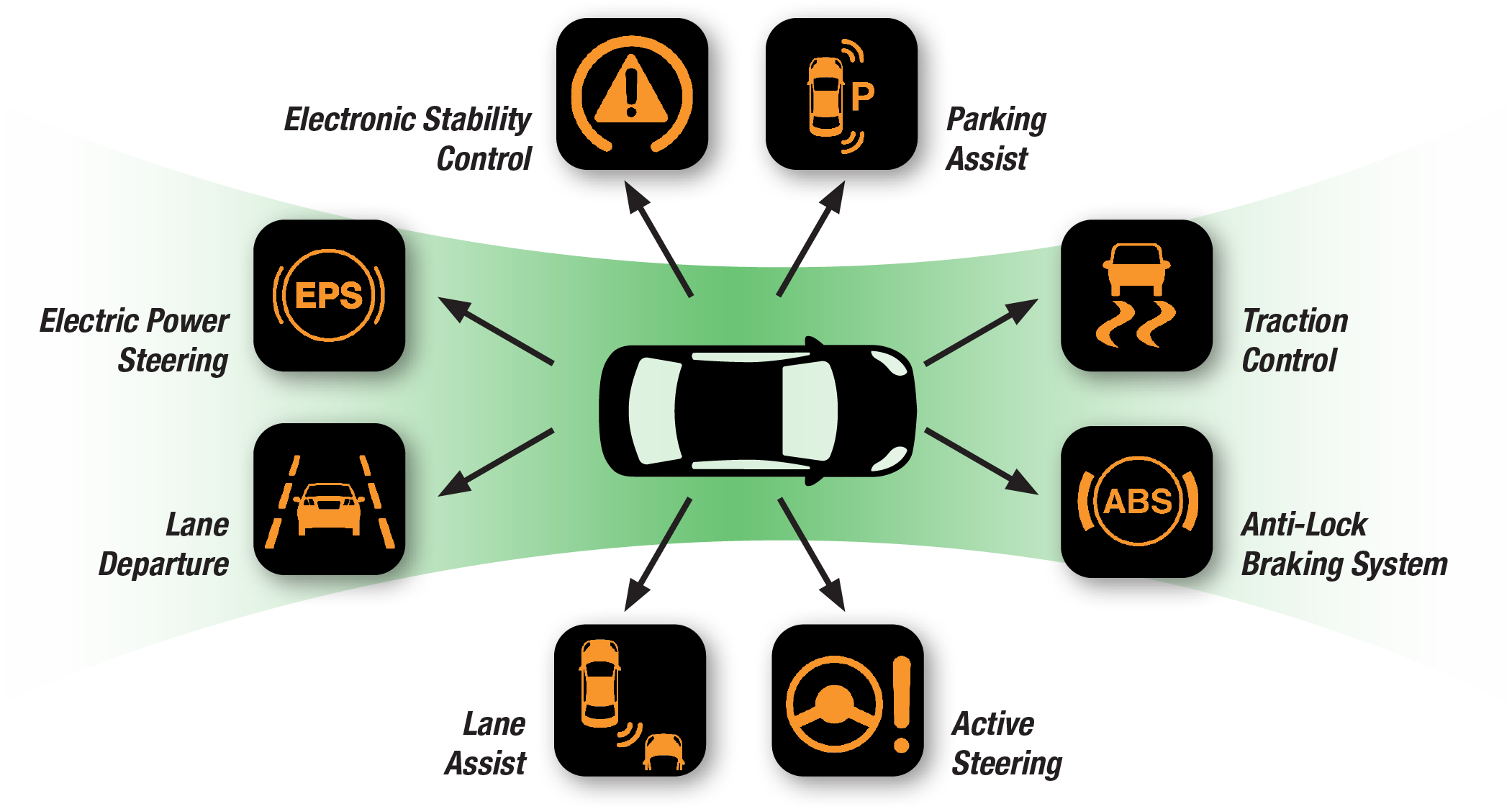
Common ADAS Features
ADAS features, also known as ADAS applications, are safety-specific technologies integrated into modern vehicles. These functionalities are designed to provide real-time warnings and automated interventions based on surrounding environments.

ESC
Electronic stability controlESC helps avoid crashes and rollovers caused by oversteering or understeering a vehicle. It measures the driver input and compares it to the lateral force, yaw rate and individual wheel speed of the vehicle.

EPS
Electronic power steeringAn electronic motor and control module provides steering assistance to the driver when needed. Data is gathered from inputs such as vehicle speed sensors, traction and stability control systems, and torque sensor.

ACC
Adaptive cruise controlACC is an optional cruise control system that automatically adjusts vehicle speed to maintain a safe distance from vehicles ahead. The driver may also set the desired gap by pressing a button to cycle among short, medium and long following distances.
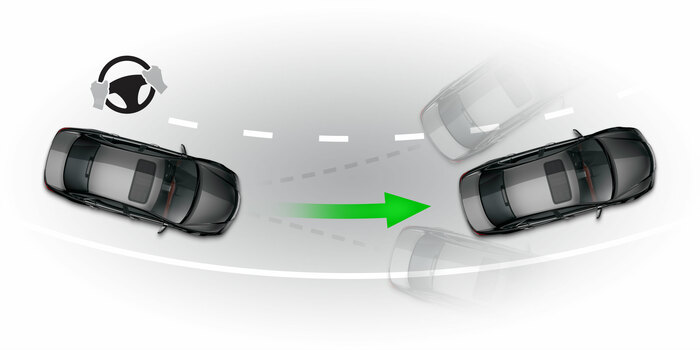

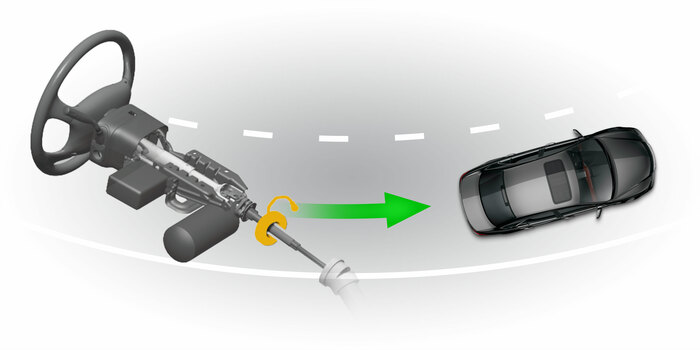
AFS
Active front steeringAFS electronically varies the degree of responsiveness between the steering wheel and the front wheels. AFS is designed to increase the steering/front wheel turning ratio at low speeds and decrease the ratio at high speeds.
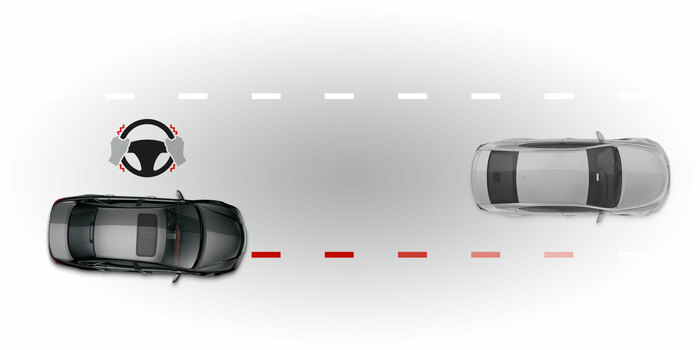
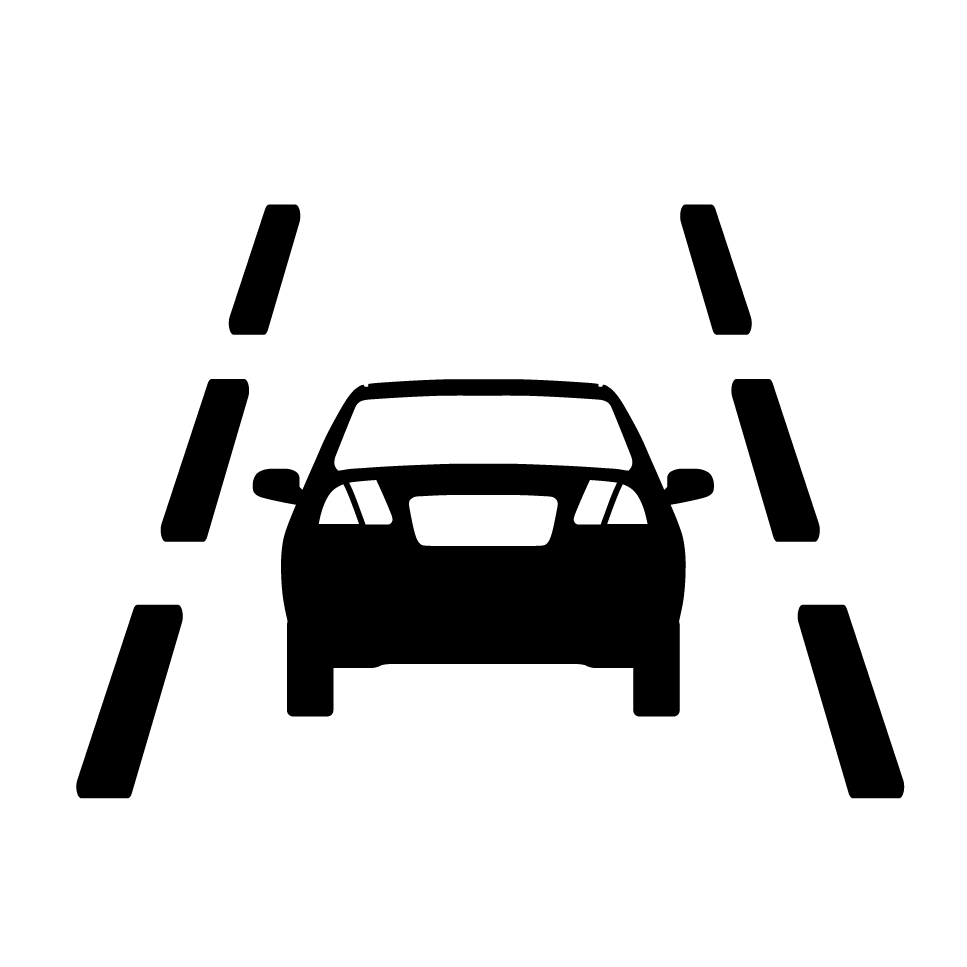
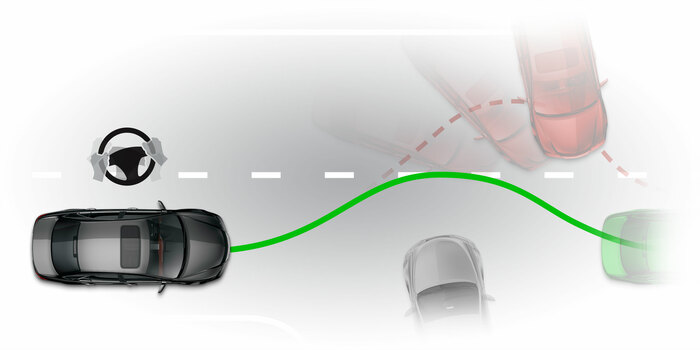
LDW
Lane departure warningLDW system detects lane markings and warns the driver if the lane is left without signaling. Advanced verisons steer the vehicle back into the lane.
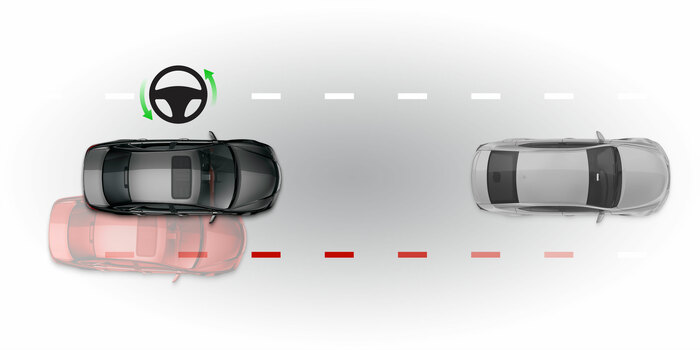
LKS
Lane keeping systemLKS technology uses cameras to oversee vehicle's lane position. It helps the car stay centered in the lanes.
Additional ADAS Features
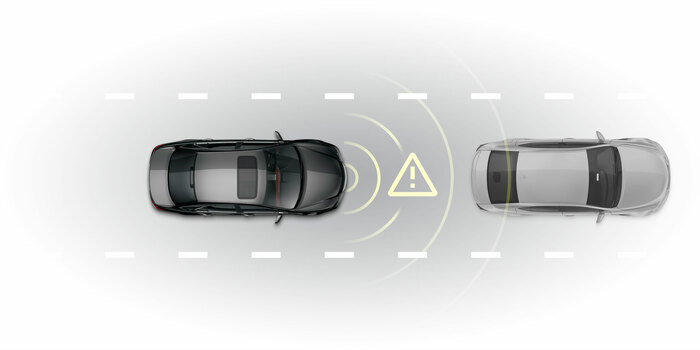
FCW
Forward collision warningFCW is designed to avoid or reduce the severity of an accident. It uses radar, cameras and sometimes lasers to detect an imminent crash.
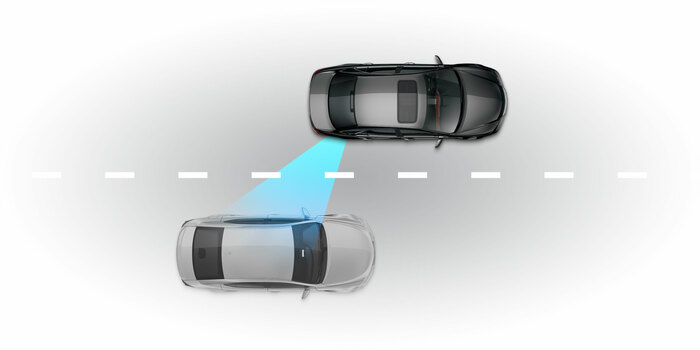

BSM
Blind spot monitoringBSM alerts the driver if another vehicle is in the blind spot when changing lanes. This technology can be found on the sideview mirror.
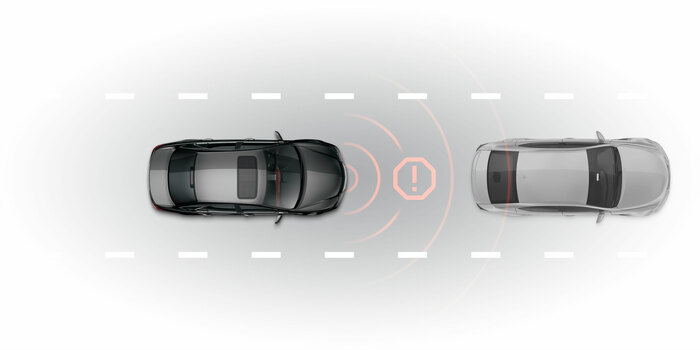

AEB
Automatic emergency brakingThe AEB function detects an impending forward crash with another vehicle and applies brakes in time to avoid or mitigate the crash.
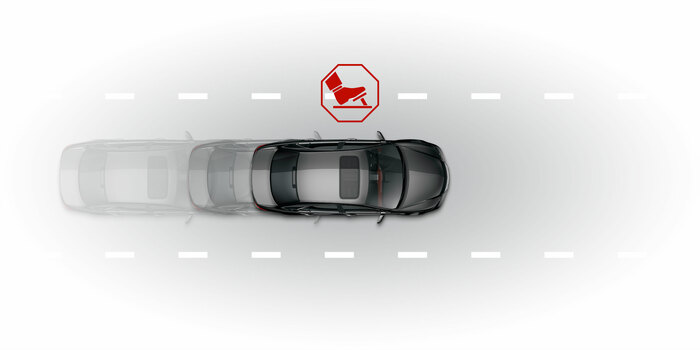
ABS
Anti-lock braking systemABS prevents the vehicle's wheels from locking up and helps keeps the car from skidding when the brakes are applied with force.
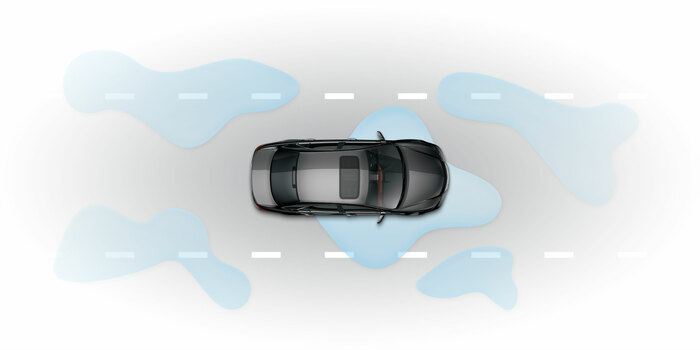
TSC
Traction control systemTraction control is designed to prevent a vehicle’s wheels from spinning on slippery surfaces.

APA
Automatic parking assistAnd APA system uses radar, sensors and camera to take autonomous control of parking a vehicle.
Did you know?
ADAS & manufacturer terminology
Automakers have their own branded safety feature terms, and names for the same functionality differ widely throughout the industry. For example, adaptive cruise control technology may be also be referred to as smart cruise control, intelligent cruise control or traffic-awareness cruise control. This lack of standardization causes confusion for consumers and technicians alike.
How ADAS Works
Advanced driver-assistance systems work by using a combination of cameras, radar, ultrasonic sensors and other inputs to create a fusion of information on the vehicle's environment to alert the driver or take corrective action as necessary.
Cameras
ADAS systems designed to keep the vehicle within the lane markers use a camera to determine the vehicle's position. Cameras are usually located against the windshield glass or around the rearview mirror. Cameras aid in lane departure warning, surround view, and surround view park assistance.
Ultrasound sensors
Many ADAS systems utilize ultrasound sensors to measure the proximity of objects nearby and take any needed corrective action. Sensors assist in applications like parking assistance.
Radars
Radar supplies the needed information for detecting surrounding objects for multiple ADAS systems, such as collision avoidance, cross-traffic alert and adaptive cruise control.
What is ADAS Calibration?
Calibration is the necessary periodic maintenance that ensures the systems are working properly.
ADAS calibration is the critically precise placement, alignment and testing of electronic sensors. The goal of ADAS calibration is to ensure these components have correct data input to respond accurately and effectively to the car’s surroundings.
Miscalibrated ADAS components can have a serious impact on vehicle safety.
When is ADAS calibration required?
ADAS calibration is needed whenever a vehicle sensor or camera is disturbed in any way, whether damaged or undamaged. ADAS components can be impacted by the following:
Collison
Fender bender
Windshield replacement
Wheel alignment
Suspension repair
Tire replacement
Sensor brake replacement
Front airbag deployment
Types of ADAS calibration: Static vs. dynamic
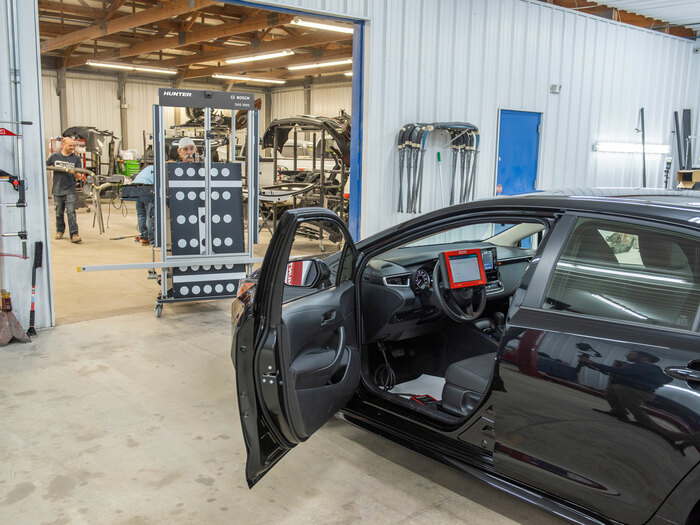

Static calibration
Static calibration refers to calibration taking place when the vehicle is parked. This type of calibration is specifically tailored for a workshop environment.

Dynamic calibration
Dynamic calibration refers to calibrations performed when the vehicle is driving, or in motion. A full ADAS calibration can be performed with a hand-held device plugged directly into the vehicle.
Site Requirements

It's a popular misconception that ADAS calibration tools require huge floor space.
Most vehicles will not need all ADAS functions adjusted at the same time, so simultaneous front, side and rear views are rarely necessary.
When multiple systems do require service, the vehicle can be repositioned within the existing space for each individual calibration.
1. Minimum floor space — 25 ft. x 34 ft.
2. Recommended floor space — 30 ft. x 45 ft.
3. Optimal floor space — 40 ft. x 60 ft.
Did you know?
ADAS calibration & OEM shop space
Different OEMs recommend or require different shop space for ADAS calibrations. However, the largest share of calibrations can be perfomed in 10 feet or less for multiple OEMs.
Future of ADAS
Today, more than 60 million vehicles have ADAS components, and that number will only increase: AAA states that 96 percent of 2020 vehicle models came equipped with at least one ADAS function. In 2023 automatic emergency braking will be required, while the government already mandates other safety-related features, such as antilock braking, electronic stability control and back-up cameras. Unless you find yourself working on a Nash Rambler, it’s likely best to assume ADAS.
Further Advancements
New capabilities derived from artifical intelligence and machine learning will play a major role in the next level of safety systems.
Rise in ADAS Calibrations
At least one-third of these vehicles will need calibration following common services, such as a wheel alignment.
ADAS Market Growth
The global ADAS market is expected to grow from 42.62 billion in 2022 to 124.31 billion by 2029.
FAQ



